There may occur some situations sometimes where data needs to be fetched from three or more tables. This article deals with two approaches to achieve it.
Example:
Creating three tables:
- student
- marks
- details
Note: Click on image if not clear to view in bigger size.
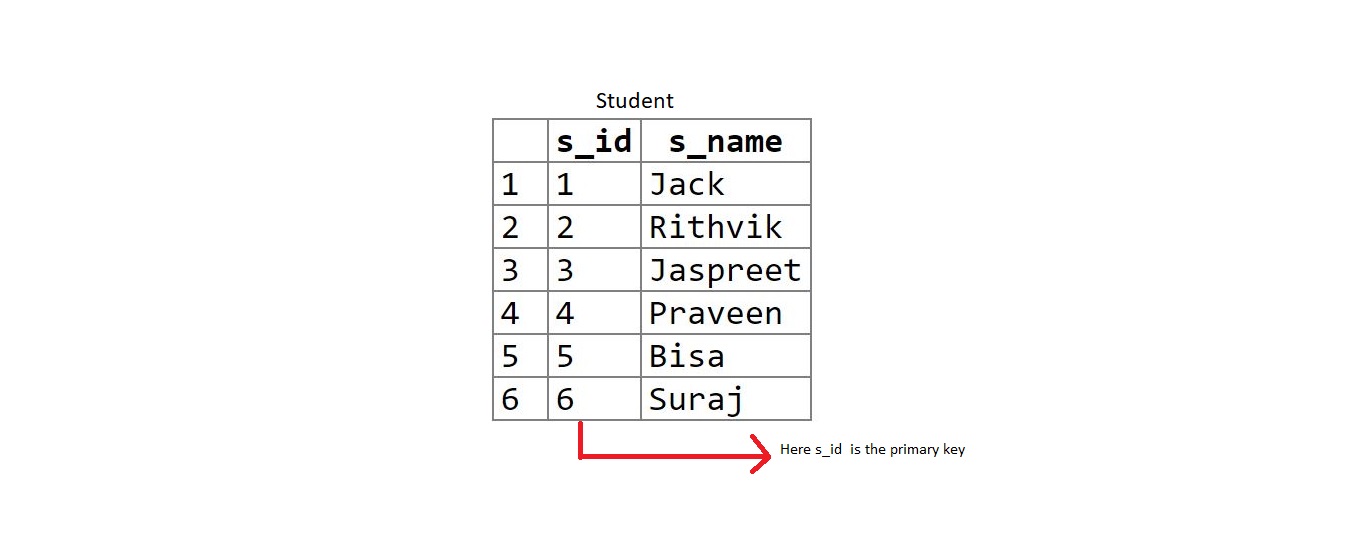
Table 1: student
create table student(s_id int primary key,
s_name varchar(20));
insert into student values(1, 'Jack');
insert into student values(2, 'Rithvik');
insert into student values(3, 'Jaspreet');
insert into student values(4, 'Praveen');
insert into student values(5, 'Bisa');
insert into student values(6, 'Suraj');
Table 2: marks
create table marks(school_id int primary key, s_id int,
score int, status varchar(20));
insert into marks values(1004, 1, 23, 'fail');
insert into marks values(1008, 6, 95, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1012, 2, 97, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1016, 7, 67, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1020, 3, 100, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1025, 8, 73, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1030, 4, 88, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1035, 9, 13, 'fail');
insert into marks values(1040, 5, 16, 'fail');
insert into marks values(1050, 10, 53, 'pass');
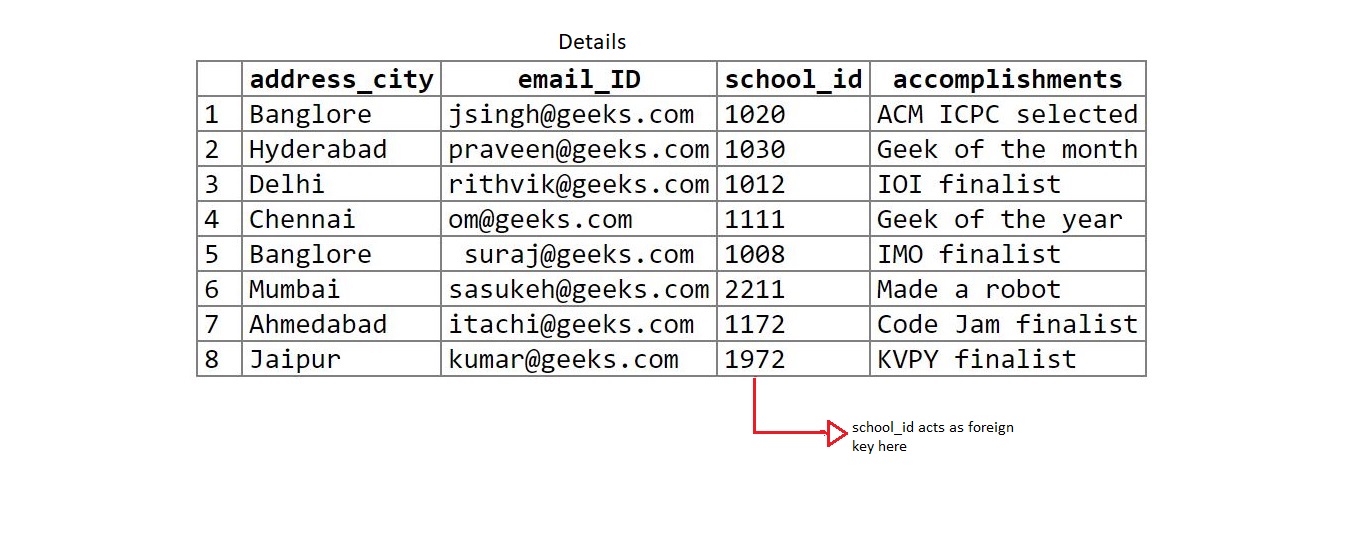
Table 3: details
create table details(address_city varchar(20), email_ID varchar(20),
school_id int, accomplishments varchar(50));
insert into details values('Banglore', 'jsingh@geeks.com',
1020, 'ACM ICPC selected');
insert into details values('Hyderabad', 'praveen@geeks.com',
1030, 'Geek of the month');
insert into details values('Delhi', 'rithvik@geeks.com',
1012, 'IOI finalist');
insert into details values('Chennai', 'om@geeks.com',
1111, 'Geek of the year');
insert into details values('Banglore', ' suraj@geeks.com',
1008, 'IMO finalist');
insert into details values('Mumbai', 'sasukeh@geeks.com',
2211, 'Made a robot');
insert into details values('Ahmedabad', 'itachi@geeks.com',
1172, 'Code Jam finalist');
insert into details values('Jaipur', 'kumar@geeks.com',
1972, 'KVPY finalist');
Two approaches to join three or more tables:
1. Using joins in sql to join the table:
The same logic is applied which is done to join 2 tables i.e. minimum number of join statements to join n tables are (n-1).
Query:
select s_name, score, status, address_city, email_id, accomplishments from student s inner join marks m on s.s_id = m.s_id inner join details d on d.school_id = m.school_id;
2. Using parent-child relationship:
This is rather an interesting approach. Create column X as primary key in one table and as foreign key in another table (i.e creating a parent-child relationship).
Let’s look in the tables created:
s_id is the primary key in student table and is foreign key in marks table. (student (parent) – marks(child)).
school_id is the primary key in marks table and foreign key in details table. (marks(parent) – details(child)).
Query:
select s_name, score, status, address_city, email_id, accomplishments from student s, marks m, details d where s.s_id = m.s_id and m.school_id = d.school_id;
<?php
$conn = mysqli_connect('localhost','root','','multiple_table');
if ($conn) {
// echo 'coneected';
}
else
{
echo 'connection failed';
}
$sql = "select s_name, score, status, address_city, email_id,
accomplishments from student s inner join marks m on
s.s_id=2 && s.s_id = m.s_id inner join details d on
d.school_id = m.school_id ";
$result = mysqli_query($conn,$sql);
while($rows=mysqli_fetch_array($result))
{
echo $rows['s_name'].'<br>';
echo $rows['address_city'].'<br>';
}
//select all 3 table data when mattching a rows
$sql = "select m.*,s.*,d.* from student s inner join marks m on
s.s_id=2 && s.s_id = m.s_id inner join details d on
d.school_id = m.school_id ";
?>





0 Comments